Multiple Choice
Identify the
letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
| 1. | Which
of the following statements are CORRECT?
1. | For gas phase equilibria, the partial pressures of reactants
and products are equal. | 2. | For a chemical system at equilibrium, the forward and reverse
rates of reaction are equal. | 3. | For an aqueous chemical system at equilibrium, the
concentrations of products divided by the concentrations of reactants equals
one. | | |
a. | 1
only | b. | 2
only | c. | 3
only | d. | 1 and
2 | e. | 1, 2, and
3 | | |
|
|
| 2. | Which
of the following statements are always CORRECT?
1. | Product concentrations appear in the numerator of an
equilibrium constant expression. | 2. | A reaction favors the formation of products if K >>
1. | 3. | Equilibrium
constants have units of atmospheres for gas phase reactions. | | |
a. | 1 only | b. | 2
only | c. | 3
only | d. | 1 and
2 | e. | 1, 2, and
3 | | |
|
|
| 3. | Write
the expression for Kc for the reaction below.
Cu2+(aq) + 4 NH3(aq) «Cu(NH3)42+(aq)
a. | Kc =
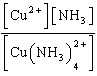 | b. | Kc =
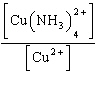 | c. | Kc =
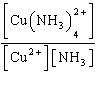 | d. | Kc =
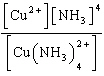 | e. | Kc =
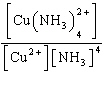 | | |
|
|
| 4. | Write
the expression for K for the reaction below.
Al2S3(s) « 2
Al3+(aq) + 3 S2-(aq)
a. | K =
[Al3+]2[S2-]3 | b. | K =
[Al3+][S2-] | c. | K = [2 Al3+][3
S2-] | d. | K = 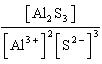 | e. | K = 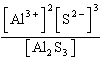 | | |
|
|
| 5. | Write
the expression for Kp for the reaction below.
2 HBr(g) « H2(g) + Br2(l)
a. | Kp = 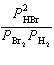 | b. | Kp = 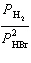 | c. | Kp = 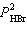 | d. | Kp = 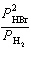 | e. | Kp = 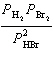 | | |
|
|
| 6. | Write
a balanced chemical equation which corresponds to the following equilibrium constant
expression.
Kp = 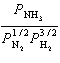
a. | 1/2
N2(g) + 3/2 H2(g) «NH3(g) | b. | N2(g)
+ 3 H2(g) « 2 NH3(g) | c. | 2
NH3(g) « N2(g) + 3 H2(g) | d. | NH3(g) « 1/2 N2(g) + 3/2 H2(g) | e. | 2
N2(g) + 6 H2(g) « 4 NH3(g) | | |
|
|
| 7. | Write
a balanced chemical equation which corresponds to the following equilibrium constant
expression.
K =
[Fe3+][OH-]3
a. | FeOH2+(s) «Fe3+(aq) +
OH-(aq) | b. | 3 Fe3+(aq) + 3 OH-(aq) «3
Fe(OH)3(aq) | c. | Fe(OH)3(aq) «Fe3+(aq) + 3 OH-(aq) | d. | Fe(OH)3(s) « Fe3+(aq) + 3 OH-(aq) | e. | Fe3+(aq) + 3 OH-(aq) « 3 Fe(OH)3(s) | | |
|
|
| 8. | For
which one of the following reactions does Kp equal
Kc? a. | 2 SO2(g) + O2(g) « 2
SO3(g) | b. | 2 O3(g) « 3 O2(g) | c. | 2
Ag2O(s) «4 Ag(s) + O2(g) | d. | 2
NH3(g) «3 H2(g) + N2(g) | e. | CO(g) +
NO2(g) « NO(g) + CO2(g) | | |
|
|
| 9. | What
is the relationship between Kp and Kc for the reaction
below?
CS2(g) + 3 Cl2(g) «S2Cl2(g) + CCl4(g)
a. | Kc = 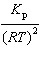 | b. | Kc = 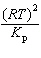 | c. | Kc = (RT)2Kp | d. | Kc = 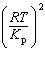 | e. | Kc = 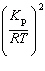 | | |
|
|
| 10. | Dinitrogen tetraoxide decomposes to nitrogen dioxide.
N2O4(g) « 2
NO2(g)
Calculate the value of Kp, given
that Kc = 5.88 ´ 10-3 at 273 K. (R = 0.08206
L·atm/mol·K) a. | 2.62 ´ 10-4 | b. | 0.132 | c. | 7.59 | d. | 1.70 ´ 102 | e. | 3.81
´
10-3 | | |
|
|
| 11. | If
the reaction quotient, Q, is greater than Kp, then a. | the chemical
system has reached equilibrium. | b. | the temperature must be increased for the reaction to proceed
in the forward direction. | c. | the reaction will proceed in the direction that results in
fewer gas phase particles. | d. | the reaction will proceed to the right until equilibrium is
established. | e. | the reaction will proceed to the left until equilibrium is
established. | | |
|
|
| 12. | A
4.00 L flask is filled with 0.75 mol SO3, 2.50 mol SO2, and 1.30 mol
O2, and allowed to reach equilibrium. Predict the effect on the concentrations of
SO3 as equilibrium is achieved by using Q, the reaction quotient. Assume the
temperature of the mixture is chosen so that Kc = 12.
2 SO3(g) « 2 SO2(g) +
O2(g)
a. | [SO3] will decrease because Q >
K. | b. | [SO3] will decrease because Q <
K. | c. | [SO3] will increase because Q <
K. | d. | [SO3] will increase because Q >
K. | e. | [SO3] will remain the same because Q =
K. | | |
|
|
| 13. | Consider the reaction A(g) « 2 B(g) where Kp = 5.0 at 25 °C. If 0.50 mol A
and 2.0 mol B are introduced into a 1.0 L flask at 25 °C, what change in concentrations (if any) will occur in
time? a. | [A] will
decrease and [B] will decrease. | b. | [A] will decrease and [B] will
increase. | c. | [A] will increase and [B] will
increase. | d. | [A] will increase and [B] will
decrease. | e. | [A] and [B] remain unchanged. | | |
|
|
| 14. | The
reaction below is studied at a high temperature.
PCl5(g) «PCl3(g) +
Cl2(g)
At equilibrium, the partial pressures of the gases are
as follows: PCl5 = 1.8 ´ 10-2 atm, PCl3 = 5.6 ´ 10-2
atm, and Cl2 = 3.8 ´ 10-4 atm. What is the value of Kp for
the reaction? a. | 3.8 ´
10-7 | b. | 1.2 ´ 10-3 | c. | 3.1 | d. | 8.5 ´ 102 | e. | 2.6 ´
106 | | |
|
|
| 15. | Excess Ca(IO3)2(s) is placed in 1.5 L of water. At equilibrium,
the solution contains 0.011 M IO3-(aq). What is the equilibrium constant for
the reaction below?
Ca(IO3)2(s) «
Ca2+(aq) + 2 IO3-(aq)
a. | 3.3 ´
10-7 | b. | 6.7 ´ 10-7 | c. | 1.3 ´
10-6 | d. | 5.3 ´ 10-6 | e. | 6.1 ´
10-5 | | |
|
|
| 16. | At 25
°C, only 1.9 g
CaSO4 will dissolve in 2.00 L of water. What is the equilibrium constant for the reaction
below?
CaSO4(s) «Ca2+(aq) + SO42-(aq)
a. | 4.9 ´
10-5 | b. | 1.9 ´ 10-4 | c. | 1.4 ´
10-2 | d. | 7.0 10-3 | e. | 0.90 | | |
|
|
| 17. | We
place 0.0774 mol N2O4(g) in a 1.00 L flask at a given temperature. After
reaching equilibrium, the concentration of NO2(g) is 0.0068 M. What is
Kc for the reaction below?
N2O4(g)«2 NO2(g)
a. | 8.8 ´
10-5 | b. | 5.9 ´ 10-4 | c. | 6.2 ´
10-4 | d. | 7.2 10-4 | e. | 9.6 ´
10-2 | | |
|
|
| 18. | A
sealed tube is prepared with 1.07 atm PCl5 at 500 K. The PCl5 decomposes until
equilibrium is established.
PCl5(g) «PCl3(aq) + Cl2(g)
The equilibrium pressure in the tube is 1.54 atm. Calculate
Kp. a. | 0.052 | b. | 0.20 | c. | 0.27 | d. | 0.37 | e. | 2.2 | | |
|
|
| 19. | A
mixture of 0.200 mol NO2 and 0.200 mol CO is placed in a 1.00 L flask and given time to
equilibrate. Analysis of the equilibrium mixture indicates that 0.134 mol of CO2 is
present. Calculate Kc for the reaction.
NO2(g) + CO(g) «NO(g) + CO2(g)
a. | 0.27 | b. | 0.45 | c. | 0.67 | d. | 2.0 | e. | 4.1 | | |
|
|
| 20. | A
gaseous mixture of NO2 and N2O4 is in equilibrium. If the
concentration of N2O4 is 7.1 ´ 10-4 M, what is the concentration of
NO2?
2 NO2(g) «
N2O4(g) Kc = 170
a. | 1.7 ´
10-11 M | b. | 4.2 ´ 10-6 M | c. | 2.0 ´ 10-3
M | d. | 4.9 ´ 102
M | e. | 2.4 ´ 105
M | | |
|
|
| 21. | At 25
°C, the
decomposition of dinitrogen tetraoxide
N2O4(g) « 2
NO2(g)
has an
equilibrium constant (Kp) of 0.144. At equilibrium, the total pressure of the
system is 0.48 atm. What is the partial pressure of each gas? a. | 0.030 atm
NO2(g) and 0.42 N2O4(g) | b. | 0.060 atm
NO2(g) and 0.42 N2O4(g) | c. | 0.16 atm
NO2(g) and 0.18 N2O4(g) | d. | 0.20 atm
NO2(g) and 0.28 N2O4(g) | e. | 0.28 atm
NO2(g) and 0.20 N2O4(g) | | |
|
|
| 22. | The
equilibrium constant at 25 °C for the dissolution of silver bromide is 5.4 ´
10-13.
AgBr(s) «Ag+(aq) +
Br-(aq)
If an excess quantity of AgBr(s) is added to water and
allowed to equilibrate, what is the equilibrium concentration of Ag+? a. | 2.9 ´
10-25 M | b. | 2.7 ´ 10-13 M | c. | 5.4 ´
10-13 M | d. | 1.1 ´ 10-12 M | e. | 7.3 ´ 10-7
M | | |
|
|
| 23. | Hydrogen iodide can decompose into hydrogen and iodine
gases.
2 HI(g) « H2(g) + I2(g)
Kp = 0.016
If 0.820 atm
HI(g) is sealed in a flask, what is the pressure of each gas when equilibrium is
established? a. | HI = 0.576 atm,
H2 = 0.096 atm, I2 = 0.096 atm | b. | HI = 0.654 atm,
H2 = 0.083 atm, I2 = 0.083 atm | c. | HI = 0.728 atm,
H2 = 0.092 atm, I2 = 0.092 atm | d. | HI = 0.737 atm,
H2 = 0.083 atm, I2 = 0.083 atm | e. | HI = 0.768 atm,
H2 = 0.111 atm, I2 = 0.111 atm | | |
|
|
| 24. | We
place 1.32 mol PCl5 in a 1.0 L flask and allow it to reach equilibrium at a given
temperature. What is the final concentration of Cl2 in the
flask?
PCl5(g)«
PCl3(aq) + Cl2(g) Kc = 0.47
a. | 0.36
M | b. | 0.59
M | c. | 0.62
M | d. | 0.79
M | e. | 85
M | | |
|
|
| 25. | The
equilibrium constant, Kc, for the following reaction is 1.0 ´ 10-5
at 1500 K.
N2(g) + O2(g) « 2
NO(g)
If 0.750 M N2 and 0.750 M O2 are
allowed to equilibrate at 1500 K, what is the concentration of NO? a. | 6.7 ´ 10-4
M | b. | 1.2 ´ 10-3
M | c. | 2.4 ´ 10-3
M | d. | 2.7 ´ 10-3
M | e. | 5.5 ´ 10-3
M | | |
|
|
| 26. | Carbonyl bromide decomposes to carbon monoxide and bromine.
COBr2(g) « CO(g) + Br2(g)
Kc is 0.19 at 73 °C. If an initial
concentration of 0.63 M COBr2 is allowed to equilibrate, what are the equilibrium
concentrations of COBr2, CO, and Br2? a. | [COBr2] = 0.11 M, [CO] = 0.26 M, [Br2] = 0.26
M | b. | [COBr2] = 0.28 M, [CO] = 0.35 M, [Br2] = 0.35
M | c. | [COBr2] = 0.30 M, [CO] = 0.33 M, [Br2] = 0.33
M | d. | [COBr2] = 0.37 M, [CO] = 0.26 M, [Br2] = 0.26
M | e. | [COBr2] = 0.63 M, [CO] = 0.35 M, [Br2] = 0.35
M | | |
|
|
| 27. | For
the following reaction,
2
SO2(g) + O2(g) «2 SO3(g)
the equilibrium constant, Kp, is 0.758 at 627
°C. What is the
equilibrium constant, at 627 °C, for the reaction below?
SO3(g) f SO2(g) + 1/2
O2(g)
a. | 0.660 | b. | 0.871 | c. | 1.15 | d. | 1.32 | e. | 1.74 | | |
|
|
| 28. | The
equilibrium constant (Kp) for the following reaction is 3.94 ´ 10-3
at a given temperature.
N2(g)
+ 2 H2O(g) « 2 NO(g) + 2 H2(g)
What is the equilibrium constant for the reaction below at the same
temperature?
3 N2(g) + 6 H2O(g) f 6
NO(g) + 6 H2(g)
a. | 6.12 ´ 10-8 | b. | 1.31
´
10-3 | c. | 3.94 ´ 10-3 | d. | 1.18
´
10-2 | e. | 1.58 ´ 10-1 | | |
|
|
| 29. | Given
the following chemical equilibria,
N2(g)
+ 3 H2(g) « 2 NH3(g) K1
4
NH3(g) + 5 O2(g) «4 NO(g) + 6 H2O(g)
K2
H2(g) + 1/2 O2(g)«
H2O(g) K3
Determine the equilibrium constant for the reaction
below.
N2(g) + O2(g) f 2 NO(g)
K4
a. | K4 = K1 ´
K2 ´ K3 | b. | K4 = K1 + K2 + K3 | c. | K4 = K1 + 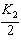 + 3K3
+ 3K3 | d. | K4 = 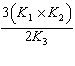 | e. | K4 = 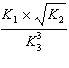 | | |
|
|
| 30. | Given
the following equilibria,
Ni2+(aq) + 2 OH-(aq) « Ni(OH)2(s) K1 = 1.8
´
1015
Ni(NH3)62+(aq) «
Ni2+(aq) + 6 NH3(aq) K2 = 5.6 ´
108
determine the
equilibrium constant for the following reaction.
Ni(OH)2(s) + 6 NH3(aq) f
Ni(NH3)62+(aq) + 2 OH-(aq)
K3
a. | 9.9 ´ 10-25 | b. | 1.8 ´
10-9 | c. | 3.1 ´ 10-7 | d. | 3.2 ´
106 | e. | 1.0 ´ 1024 | | |
|
|
| 31. | Assume that the following chemical reaction is at
equilibrium.
I2(g) + Cl2(g) « 2 ICl(g)
DH° = -26.9 kJ
At 25 °C, Kp = 2.0 ´ 105.
If the temperature is decreased to 5 °C, which statement applies? a. | Kp will decrease and the reaction will proceed in the forward
direction. | b. | Kp will decrease and the reaction will
proceed in the backward direction. | c. | Kp will remain unchanged and the reaction
will proceed in the forward direction. | d. | Kp will remain unchanged and the reaction
will proceed in the backward direction. | e. | Kp will increase and the reaction will
proceed in the forward direction. | | |
|
|
| 32. | Assume that the following endothermic chemical reaction is at
equilibrium.
C(s) + H2O(g) «
H2(g) + CO(g)
Which of the
following statements are CORRECT?
1. | Increasing the amount of C(s) will increase the equilibrium
concentration of CO(g). | 2. | Increasing the temperature will increase the equilibrium
concentration of H2(g). | 3. | Decreasing the concentration of H2O(g) will increase
the equilibrium concentration of CO(g). | | |
a. | 1
only | b. | 2
only | c. | 3
only | d. | 1 and
2 | e. | 1, 2, and
3 | | |
|
|
| 33. | The
thermochemical equation for the formation of ammonia from elemental nitrogen and hydrogen is as
follows.
N2(g) + 3 H2(g) « 2
NH3(g) DH = -92.2 kJ
Which of the
following will drive the equilibrium system to the right? a. | adding
NH3(g) | b. | removing N2(g) | c. | increasing the
volume of the reaction vessel | d. | increasing the temperature | e. | adding
H2(g) | | |
|
|
| 34. | In
which of the following equilibrium systems will an increase in the pressure have NO effect on the
concentrations of products and reactants? a. | CaO(s) + CO2(g) «CaCO3(s) | b. | N2(g) + 3 H2(g) « 2
NH3(g) | c. | H2(g) + Cl2(g) « 2
HCl(g) | d. | H2(g) + CO2(g) «CO(g) +
H2O(l) | e. | 2 H2O2(g) « 2
H2O(g) + O2(g) | | |
|
|
| 35. | A
flask contains the following chemical system at equilibrium.
Ca(OH)2(s) « Ca2+(aq) + 2
OH-(aq)
Addition of which of the following substances will
increase the solubility of Ca(OH)2(s)? a. | HNO3(aq) | b. | Ca(OH)2(s) | c. | NaOH(s) | d. | CaCl2(s) | e. | Ca(NO3)2(s) | | |
|