Multiple Choice
Identify the
letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
| 1. | What
is the effect of adding 10 mL of 0.1 M NaOH(aq) to 100 mL of 0.2 M
NH4+(aq)?
1. | The pH will decrease. | 2. | The concentration of NH3 will
increase. | 3. | The
concentration of NH4+ will decrease. | | |
a. | 1 only | b. | 2
only | c. | 3
only | d. | 2 and
3 | e. | 1, 2, and
3 | | |
|
|
| 2. | What
is the pH of a solution that results from adding 25 mL of 0.15 M HCl to 25 mL of 0.52 M
NH3? (Kb of NH3 = 1.8 ´
10-5) a. | 2.74 | b. | 4.35 | c. | 9.65 | d. | 11.26 | e. | 11.41 | | |
|
|
| 3. | Which
of the following combinations would be best to buffer an aqueous solution at a pH of
2.0? a. | H3PO4 and H2PO4-,
Ka1 = 7.5 ´ 10-3 | b. | HNO2
and NO2-, Ka = 4.5 ´ 10-4 | c. | CH3CO2H and CH3COO-, Ka
= 1.8 ´
10-5 | d. | H2PO4- and
HPO42-, Ka2 = 6.2 ´ 10-8 | e. | NH4+ and NH3, Ka = 5.7 ´
10-10 | | |
|
|
| 4. | Which
of the following combinations would be the best to buffer an aqueous solution at a pH of
5.0? a. | H3PO4 and H2PO4-,
Ka1 = 7.5 ´ 10-3 | b. | HNO2
and NO2-, Ka = 4.5 ´ 10-4 | c. | CH3CO2H and CH3COO-, Ka
= 1.8 ´
10-5 | d. | H2PO4- and
HPO42-, Ka2 = 6.2 ´ 10-8 | e. | NH4+ and NH3, Ka = 5.7 ´
10-10 | | |
|
|
| 5. | Each
of the following mixtures can produce an effect buffer solution EXCEPT a. | HClO4
and NaClO4. | b. | HF and NaF. | c. | NaHCO3 and Na2CO3. | d. | Na2HPO4 and
Na3PO4. | e. | NH4Cl and NH3. | | |
|
|
| 6. | All
of the following statements concerning buffers are true EXCEPT a. | buffers are
resistant pH changes upon addition of small quantities of strong acids or
bases. | b. | buffers are used as colored indicators in acid-base
titrations. | c. | the pH of a buffer is close to the pKa of the
weak acid from which it is made. | d. | buffers contain appreciable quantities of a weak acid and its
conjugate base. | e. | buffers are resistant to changes in pH when diluted with
water. | | |
|
|
| 7. | Which
of the following mathematical expressions is the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation? a. | pKa = pH + log 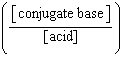 | b. | pH = pKa + log 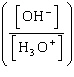 | c. | pH =
pKa + log 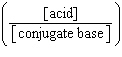 | d. | pKa = pH - log 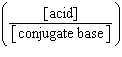 | e. | pH =
pKa + log 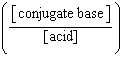 | | |
|
|
| 8. | What
is the pH of the buffer that results when 4.0 g of NH3 and 8.0 g of NH4Cl are
diluted with water to a volume of 0.50 L? (Ka of NH4+ = 5.6
´
10-10) a. | 8.95 | b. | 9.06 | c. | 9.25 | d. | 9.45 | e. | 9.55 | | |
|
|
| 9. | What
mass of solid KF (molar mass = 58.1 g/mol) should be added to 2.0 L of 0.25 M HF to make a buffer
with a pH of 3.14? (pKa for HF = 3.14) a. | 7.3
g | b. | 15
g | c. | 29
g | d. | 58
g | e. | 120
g | | |
|
|
| 10. | If
the ratio of acid to base in a buffer increases by a factor of 10, the pH of the
buffer a. | decreases by
1. | b. | decreases by
10. | c. | increases by
10. | d. | increases by
1. | e. | remains
unchanged. | | |
|
|
| 11. | A
buffer is prepared by combining 250 mL of 0.25 M NaOH and 250 mL of a 0.600 M weak acid, HA. If the
pH of the buffer is 6.33, what is the pKa of the acid? a. | 5.95 | b. | 6.18 | c. | 6.33 | d. | 6.48 | e. | 6.71 | | |
|
|
| 12. | How
many moles of HCl must be added to 1.00 L of 0.72 M NH3 to make a buffer with a pH of
9.50? (Ka of NH4+ = 5.6 ´
10-10) a. | 0.26
mol | b. | 0.31
mol | c. | 0.41
mol | d. | 0.46
mol | e. | 1.3
mol | | |
|
|
| 13. | Which
one of the following conditions is always met at the equivalence point of the titration of a
monoprotic weak base with a strong acid? a. | The pH of the solution is equal to
7.00. | b. | The volume of acid added from the buret equals the volume of
base titrated. | c. | The molarity of the acid equals the initial molarity of the
weak base. | d. | The percent ionization of the acid equals the percent
ionization of the base. | e. | The moles of acid added from the buret equals the initial moles
of weak base. | | |
|
|
| 14. | Which
one of the following conditions is always true for a titration of a weak acid with a strong
base? a. | A colored
indicator with a pKa less than 7 should be used. | b. | If a colored
indicator is used, it must change color rapidly in the weak acid's buffer
region. | c. | Equal volumes of weak acid and strong base are required to
reach the equivalence point. | d. | The equivalence point occurs at a pH equal to
7. | e. | The equivalence
point occurs at a pH greater than 7. | | |
|
|
| 15. | A
volume of 25.0 mL of 0.100 M HCO2H(aq) is titrated with 0.100 M NaOH(aq). What is the pH
after the addition of 12.5 mL of NaOH? (Ka for HCO2H = 1.8 ´
10-4) a. | 2.52 | b. | 3.74 | c. | 4.74 | d. | 7.00 | e. | 10.26 | | |
|
|
| 16. | A
25.0 mL sample of 0.0200 M NH3(aq) is titrated with 0.0100 M HCl(aq). What is the pH at
the equivalence point? (Kb of NH3 = 1.8 ´
10-5) a. | 3.46 | b. | 5.48 | c. | 5.72 | d. | 8.25 | e. | 10.54 | | |
|
|
| 17. | A
50.0 mL sample of 0.0240 M NH3(aq) is titrated with aqueous hydrochloric acid. What is the
pH after the addition of 15.0 mL of 0.0600 M HCl(aq)? (Kb of NH3 = 1.8
´
10-5) a. | 8.78 | b. | 8.86 | c. | 9.25 | d. | 9.38 | e. | 9.73 | | |
|
|
| 18. | Potassium hydrogen phthalate (molar mass = 204.2 g/mol) is used to standardize sodium
hydroxide. If 26.37 mL of NaOH(aq) is required to titrate 0.7719 g KHP to the equivalence point, what
is the concentration of the NaOH(aq)?
HC8H4O4-(aq) +
OH-(aq) f C8H4O42-(aq) +
H2O(l)
a. | 0.02036 M | b. | 0.02937
M | c. | 0.09968
M | d. | 0.1433
M | e. | 5.977
M | | |
|
|
| 19. | A
50.0 mL sample of vinegar is titrated with 0.774 M NaOH(aq). If the titration requires 41.6 mL of
NaOH(aq), what is the concentration of acetic acid in the vinegar? a. | 0.0921
M | b. | 0.429
M | c. | 0.644
M | d. | 0.930
M | e. | 0.967
M | | |
|
|
| 20. | An
impure sample of sodium carbonate, Na2CO3, is titrated with 0.150 M HCl
according to the reaction below.
2 HCl(aq) +
Na2CO3(aq) f CO2(g) + H2O(l) + 2
NaCl(aq)
What is the percent of Na2CO3 in
a 0.927 g sample if the titration requires 27.3 mL of HCl? The molar mass of
Na2CO3 is 106.0 g/mol. a. | 0.221% | b. | 23.4% | c. | 46.8% | d. | 93.7% | e. | 104% | | |
|
|
| 21. | Which
is the best colored indicator to use in the titration of 0.0010 M
CH3CO2-(aq) with HCl(aq)? Why? (Kb of
CH3CO2- = 5.6 ´ 10-10)
Indicator | p K a | Bromocresol green | 4.7 | Phenol
Red | 7.8 | Phenolphthalein | 9.0 | | |
a. | Bromocresol green. The pH at the equivalence point is less than
7.0. | b. | Phenol Red. The
pKb of acetate ion and the pKb of the indicator are
similar. | c. | Phenol Red. The equivalence point of an acid-base titration
occurs at a pH of 7.0. | d. | Phenolphthalein. The pKb of acetate ion and
the pKb of the indicator are similar. | e. | Phenolphthalein.
The pH at the equivalence point is greater than 7.0. | | |
|
|
| 22. | What
color change is exhibited by phenolphthalein during a titration of aqueous acetic acid with aqueous
sodium hydroxide? a. | colorless to
pink | b. | pink to
colorless | c. | green to yellow | d. | yellow to
blue | e. | blue to
yellow | | |
|
|
| 23. | Which
of the following equations is the solubility product for magnesium iodate,
Mg(IO3)2? a. | Ksp =
[Mg2+][I-]2[O2-]6 | b. | Ksp =
[Mg2+][I-]2[3O2-]2 | c. | Ksp = [Mg2+]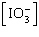 | d. | Ksp = [Mg2+]2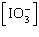 | e. | Ksp = [Mg2+]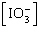 2 2 | | |
|
|
| 24. | The
solubility of SrSO4 in water is 0.107 g in 1.0 L at 25 °C. What is the
value of Ksp for SrSO4? a. | 3.4 ´
10-7 | b. | 5.8 ´ 10-4 | c. | 1.2 ´
10-3 | d. | 1.1 ´ 10-2 | e. | 2.1 ´
10-1 | | |
|
|
| 25. | The
following anions can be separated by precipitation as silver salts: Cl-, Br-,
I-, CrO42-. If Ag+ is added to a solution containing the
four anions, each at a concentration of 0.10 M, in what order will they
precipitate?
Compound | K sp | AgCl | 1.8 ´ 10 -10 | Ag 2 CrO 4 | 1.1 ´
10-12 | AgBr | 5.4 ´ 10 -13 | AgI | 8.5 ´ 10 -17 | | |
a. | AgCl ® Ag2CrO4 ® AgBr
®
AgI | b. | AgI ® AgBr
®
Ag2CrO4 ® AgCl | c. | Ag2CrO4 ® AgCl
® AgBr
®
AgI | d. | Ag2CrO4 ® AgI ® AgBr ® AgCl | e. | AgI ® AgBr ® AgCl ® Ag2CrO4 | | |
|