Multiple Choice
Identify the
letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
| 1. | Reactants A and B are placed in an empty flask. If the reaction A(g) + B(g) f 2
C(g) has Kp > 1, which of the following statements are
correct?
1. | The forward reaction is spontaneous. | 2. | The forward rate of reaction is fast. | 3. | The reaction is reactant-favored. | | |
a. | 1 only | b. | 2
only | c. | 3
only | d. | 1 and
2 | e. | 1, 2, and
3 | | |
|
|
| 2. | The
following processes occur spontaneously at 25 °C. Which of these processes are
endothermic?
1. | the combustion of methane to produce water and carbon
dioxide | 2. | the expansion of
an ideal gas into a vacuum | 3. | the melting of ice | | |
a. | 1 only | b. | 2
only | c. | 3
only | d. | 1 and
2 | e. | 2 and
3 | | |
|
|
| 3. | A
statement of the second law of thermodynamics is that a. | spontaneous
reactions are always exothermic. | b. | energy is conserved in a chemical
reaction. | c. | the Gibbs free energy is a function of both enthalpy and
entropy. | d. | DS = - DH for any chemical reaction. | e. | in a spontaneous
process, the entropy of the universe increases. | | |
|
|
| 4. | As
defined by Ludwig Boltzmann, the third law of thermodynamics states that a. | in a spontaneous
process, the entropy of the universe increases. | b. | there is no
disorder in a perfect crystal at 0 K. | c. | the total entropy of the universe is always
increasing. | d. | the total energy of the universe is
constant. | e. | mass and energy are conserved in all chemical
reactions. | | |
|
|
| 5. | Which
of the following linear chain alcohols is likely to have the highest standard entropy in the liquid
state? a. | CH3OH | b. | CH3CH2OH | c. | CH3CH2CH2OH | d. | CH3CH2CH2CH2OH | e. | CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2OH | | |
|
|
| 6. | Which
of the following processes are reversible?
1. | the expansion of an ideal gas into a
vacuum | 2. | the melting of
ice at 0 °C | 3. | the combustion of carbon to produce carbon
dioxide | | |
a. | 1
only | b. | 2
only | c. | 3
only | d. | 1 and
2 | e. | 2 and
3 | | |
|
|
| 7. | If a
chemical reaction has a positive change in entropy then a. | the change in
enthalpy is negative. | b. | the reaction is exothermic. | c. | heat goes from
the system into the surroundings. | d. | the disorder of the system increases. | e. | the reaction is
spontaneous. | | |
|
|
| 8. | Which
of the following processes involves a decrease in entropy? a. | the
decomposition of NH3(g) into H2(g) and N2(g)
gas | b. | the dissolution
of NaCl in water | c. | the condensation of steam to liquid
water | d. | the evaporation of ethanol | e. | the sublimation
of dry ice (i.e., CO2(s)) | | |
|
|
| 9. | All
of the following statements concerning entropy are true EXCEPT a. | entropy values
for substances are greater than or equal to zero. | b. | entropy is a
state function. | c. | a positive change in entropy denotes a change toward greater
disorder. | d. | entropy is zero for elements under standard
conditions. | e. | the entropy of a substance in the gas phase is greater than the
solid phase. | | |
|
|
| 10. | Which
reaction is likely to have a negative change in entropy? a. | 2
NH3(g) ® N2(g) + 3 H2(g) | b. | CaCO3(s) ® CaO(s) + CO2(g) | c. | NaCl(s)
®
Na+(aq) + Cl-(aq) | d. | N2O4(g) ® 2
NO2(g) | e. | 2 CO(g) ® 2 C(s) + O2(g) | | |
|
|
| 11. | Calculate the standard entropy change for the combustion of methanol at 25
°C.
2 CH3OH(l) + 3
O2(g) ® 2 CO2(g) + 4 H2O(g)
Species | S° (J/K×mol) | CH 3
OH (l) | 127.2 | O 2
(g) | 205.1 | CO 2
(g) | 213.7 | H 2
O(g) | 188.8 | | |
a. | -2052.3
J/K | b. | -312.9
J/K | c. | +70.2
J/K | d. | +312.9
J/K | e. | +2052.3
J/K | | |
|
|
| 12. | The
standard entropy of formation of PCl3(g) is -33.2 J/K·mol.
1/4 P4(s) + 3/2 Cl2(g) ®
PCl3(g)
Calculate the standard molar entropy of
PCl3(g) given S°[P4(s)] = 41.1 J/K·mol and S°[Cl2(g)] = 223.1 J/K·mol. a. | -378.1
J/K·mol | b. | -297.4 J/K·mol | c. | +212.2
J/K·mol | d. | +231.0 J/K·mol | e. | +311.7
J/K·mol | | |
|
|
| 13. | Predict the signs of DH and DS for the condensation of steam at 85 °C. a. | DH < 0 and DS < 0 | b. | DH < 0 and DS > 0 | c. | DH > 0 and DS < 0 | d. | DH > 0 and DS > 0 | e. | DH = 0 and DS < 0 | | |
|
|
| 14. | Hydrogen gas is a non-polluting fuel. Predict the signs of DH,
DS, and
DG for the
combustion of hydrogen gas at 150 °C.
2
H2(g) + O2(g) ® 2 H2O(g)
a. | DH < 0, DS > 0, DG < 0 | b. | DH < 0, DS < 0, DG < 0 | c. | DH < 0, DS > 0, DG < 0 | d. | DH > 0, DS < 0, DG < 0 | e. | DH > 0, DS < 0, DG > 0 | | |
|
|
| 15. | If
DG° < 0 for a reaction at all temperatures, then DH° is ____ and DS° is ____. a. | negative, positive | b. | positive,
negative | c. | negative, negative | d. | positive,
positive | e. | positive, either positive or negative | | |
|
|
| 16. | The
dissolution of ammonium nitrate occurs spontaneously in water at 25 °C. As
NH4NO3 dissolves, the temperature of the water decreases. What are the signs of
DH,
DS, and
DG for
this process? a. | DH > 0,
DS < 0,
DG >
0 | b. | DH > 0,
DS > 0,
DG >
0 | c. | DH > 0,
DS > 0,
DG <
0 | d. | DH < 0,
DS < 0,
DG <
0 | e. | DH < 0,
DS > 0,
DG >
0 | | |
|
|
| 17. | At
what temperatures will a reaction be spontaneous if DH = +158 kJ and DS = +411 J/K? a. | All temperatures
below 384 K | b. | Temperatures between 158 K and 411 K | c. | All temperatures
above 384 K | d. | The reaction will be spontaneous at any
temperature. | e. | The reaction will never be
spontaneous. | | |
|
|
| 18. | If a
process is exothermic and spontaneous, which of the following must be true? a. | DG > 0 and DH < 0 | b. | DG < 0 and DH < 0 | c. | DG < 0 and DS > 0 | d. | DH < 0 and DS > 0 | e. | DH > 0 and DS < 0 | | |
|
|
| 19. | Calculate 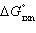 for the reaction below at 25.0 °C
for the reaction below at 25.0 °C
2
H2O(g) + S(s) ® 2 H2S(g) + O2(g)
given 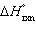 = +442.4 kJ and
= +442.4 kJ and 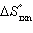 = +206.9 J/K.
= +206.9 J/K. a. | +380.7
kJ | b. | +504.1
kJ | c. | +649.3
kJ | d. | +1277.7
kJ | e. | +6.125
´ 104
kJ | | |
|
|
| 20. | All
of the following substances have a standard free energy of zero EXCEPT a. | Br2(l). | b. | I2(g). | c. | S8(s). | d. | Cl2(g). | e. | Hg(l). | | |
|
|
| 21. | Thermodynamics can be used to determine all of the following EXCEPT a. | the rate of
reaction. | b. | the extent to which a reaction
occurs. | c. | the direction in which a reaction is
spontaneous. | d. | the temperature at which a reaction is
spontaneous. | e. | the entropy change of a reaction. | | |
|
|
| 22. | For a
chemical reaction, if DG° = 0, then a. | K > 1 | b. | K =
0 | c. | K <
1 | d. | K <
0 | e. | K =
1 | | |
|
|
| 23. | All
of the following relationships are true EXCEPT a. | | b. | 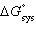 = -RT ln
(K) = -RT ln
(K) | c. | | d. | DH = 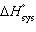 + RT ln (K)
+ RT ln (K) | e. | 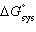 = -T
= -T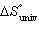 | | |
|
|
| 24. | For a
chemical system, DG° and DG are equal when a. | the system is in equilibrium. | b. | the reactants
and products are in standard state conditions. | c. | the equilibrium
constant, K, equals 0. | d. | the reaction quotient, Q, is less than
1. | e. | the reactants
and products are in the gas phase. | | |
|
|
| 25. | The
standard free energy change for a chemical reaction is -18.3 kJ/mole. What is the equilibrium
constant for the reaction at 87 °C? (R = 8.314 J/K·mol) a. | 2.2 ´
10-3 | b. | 1.0 | c. | 6.1 | d. | 4.5 ´ 102 | e. | 1.3 ´
106 | | |
|
|
| 26. | The
equilibrium constant for a reaction at 25 °C is 4.7 ´ 10-8. What is DG°? (R = 8.314 J/K·mol) a. | +1.52
kJ | b. | +3.51
kJ | c. | +6.81
kJ | d. | +18.2
kJ | e. | +41.8
kJ | | |
|